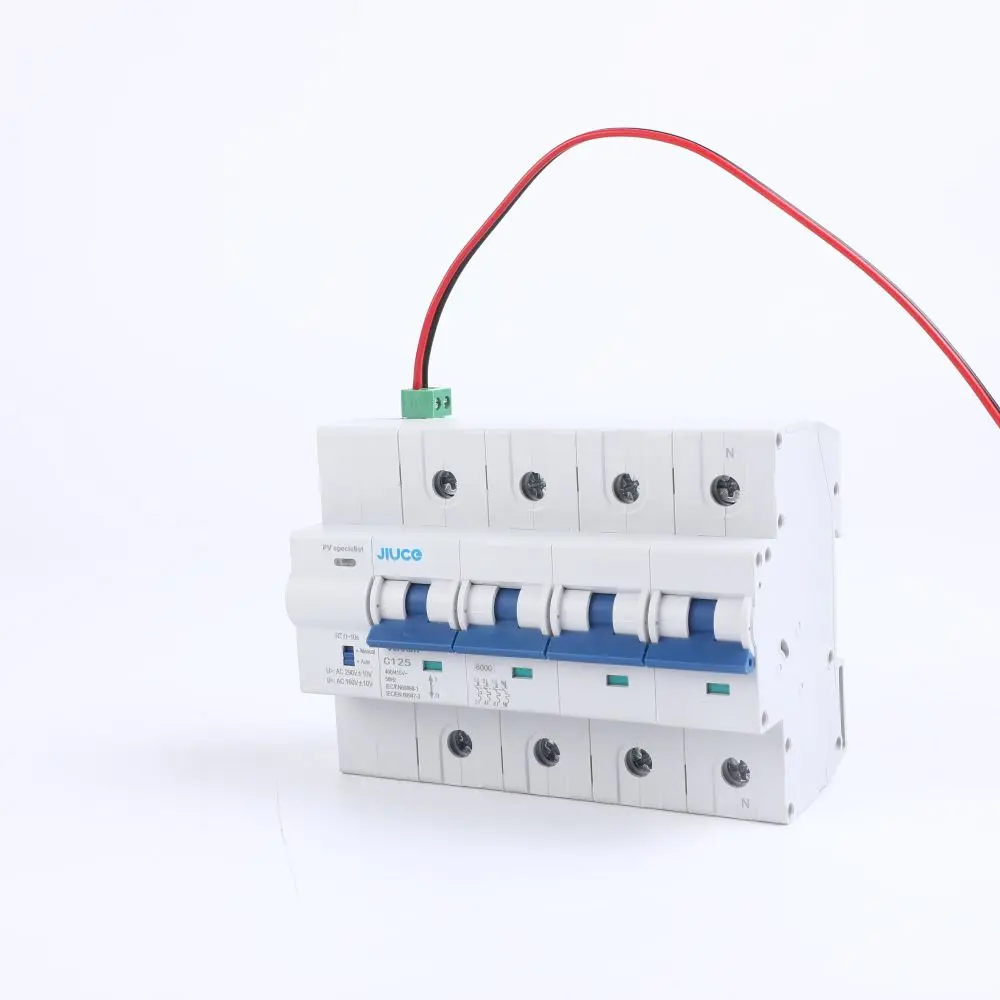
Unlocking the Technical Specifications of Molded Case Circuit Breakers
In the dynamic landscape of electrical engineering and safety protocols, Molded Case Circuit Breakers (MCCBs) emerge as indispensable guardians of electrical circuits. Abbreviated as MCCBs, these devices serve as robust barriers against overloads and short circuits, embodying a pivotal role in ensuring both safety and efficiency within electrical systems. To comprehend the nuanced intricacies of MCCBs fully, it's essential to explore the technical requirements governing their design, operation, and adherence to safety standards.


Technical Standards: The Pillars of Reliability
MCCBs operate within the framework of stringent technical standards and regulations, ensuring their reliability and adherence to safety protocols. Two cornerstone standards that delineate the prerequisites and assessment criteria for MCCBs are GOST IEC 60947-1 and GOST IEC 60947-2. Nestled within the broader IEC 60947 series, titled "Low Voltage Distribution and Control Apparatus," these standards furnish comprehensive guidelines governing the manufacturing, performance evaluation, and testing methodologies tailored specifically for MCCBs.
Scope and Application: Navigating Voltage Realms
The ambit of these standards extends to equipment designated for utilization within electrical circuits boasting nominal voltages up to 1000V AC or up to 1500V DC. Embracing an expansive array of facets, these standards establish rules and safety requisites encompassing definitions, operational parameters, design specifications, performance evaluation metrics, verification protocols, and environmental considerations.
Raw Materials and Supplies: The Foundation of Quality
Manufacturers of MCCBs are entrusted with the critical task of adhering to stringent guidelines concerning the procurement and utilization of raw materials. A meticulous control regimen is imperative to ensure uniformity and quality throughout the manufacturing continuum. Any modifications to the raw material inventory necessitate coordination and documentation to uphold the integrity of the end product. The quality control framework is meticulously calibrated to safeguard trouble-free operation throughout the designated service life of the MCCB.
Mechanical Durability: The Litmus Test
The mechanical lifespan of MCCBs serves as a litmus test for their enduring functionality. In consonance with the stipulations outlined in the standards, MCCBs are subjected to stringent durability criteria contingent on their rated current. For instance:
· MCCBs rated between 10A and 125A must endure a minimum of 15000 cycles.
· MCCBs rated between 500A and 630A should withstand a minimum of 10000 cycles.
· MCCBs rated between 1000A and 2000A are mandated to sustain a minimum of 8000 cycles.
Moreover, MCCBs are rigorously inspected to ensure their pristine condition, devoid of any rust, oxidation, or mechanical impairments, thereby ensuring optimal performance and safety.
Auxiliary Equipment Compatibility: Augmenting Functionality
The versatility of MCCBs is augmented through the seamless integration of auxiliary equipment, fostering adaptability across diverse applications. Essential auxiliary components encompass auxiliary contacts, emergency contacts, shunt release devices, motorized drives, and remote rotary handles, among others. The design architecture of MCCBs is meticulously engineered to facilitate the hassle-free installation and seamless operation of these auxiliary components, catering to a myriad of customer requirements.
Stationary (Fixed) Type Requirements: Anchored in Precision
The stationary or fixed configurations of MCCBs come replete with specific scope-of-delivery prerequisites. The standard deliverables invariably encompass interpolar dielectric dividers, elevating safety and performance benchmarks within fixed installations.
Quality Assurance and Compliance: Upholding Excellence
Premier manufacturers like W9 Group are steadfast in their commitment to quality assurance and compliance with international standards. Armed with state-of-the-art testing equipment and fortified by ISO certifications, W9 Group ensures that its MCCBs epitomize the pinnacle of quality and safety standards. A comprehensive array of testing procedures encompasses mechanical endurance, short-circuit capabilities, overload protection efficacy, flame retardancy, and component quality, thereby instilling confidence in customers regarding the reliability and safety quotient of W9 Group's MCCB offerings.
The delivery scope for the standard molded case circuit breaker of the draw-out type encompasses various components and documentation. This includes interpolar dielectric dividers for electrical safety, dielectric terminal covers to protect terminals from external factors, a comprehensive data sheet detailing technical specifications, an operating manual to guide users through installation, usage, and maintenance, a fastening kit for secure installation, an auxiliary handle for ease of operation, and a draw-out cradle for convenient installation and removal of the circuit breaker. Together, these components constitute the complete and functional delivery package.
Final Thoughts
Molded Case Circuit Breakers (MCCBs) serve as the cornerstone of electrical safety and reliability, embodying an amalgamation of robust design and stringent adherence to technical specifications. By embracing the tenets delineated within standards such as GOST IEC 60947-1 and GOST IEC 60947-2, manufacturers navigate a path toward excellence, ensuring that MCCBs uphold the highest standards of performance and safety. Through unwavering commitment to quality assurance and compliance, manufacturers like W9 Group emerge as torchbearers of innovation, catering to the evolving needs of customers worldwide with reliable, safe, and efficient MCCB solutions.

 JCB1-125
JCB1-125 JCB2-40M
JCB2-40M JCB3-63DC
JCB3-63DC JCB3-80H
JCB3-80H JCB3-80M
JCB3-80M JCBH-125
JCBH-125 JC80-2P
JC80-2P JC80-4P
JC80-4P JC125-2P
JC125-2P JC125-4P
JC125-4P JCMX
JCMX JCSD
JCSD JCOF
JCOF JCMX1-125
JCMX1-125 JCOF1-125
JCOF1-125 JCSD1-125
JCSD1-125 JCRD4-125
JCRD4-125 JCRB2-100
JCRB2-100 JCR2-63
JCR2-63 JCR1-40
JCR1-40 JCB2LE-80M
JCB2LE-80M JCB2LE-80M
JCB2LE-80M JCB2LE-80M
JCB2LE-80M JCB2LE-40M
JCB2LE-40M JCB1LE-125
JCB1LE-125 JCB3LM-80
JCB3LM-80 JCH2-125
JCH2-125 JCH2-125
JCH2-125 CJX2
CJX2 CJ19
CJ19 JCMCU
JCMCU JCHA
JCHA JC3AF-S
JC3AF-S JC3AE
JC3AE JCSD-40
JCSD-40 JCSD-60
JCSD-60 JCSP-40
JCSP-40 JCSP-60
JCSP-60 JCSPV
JCSPV WEW1-1000
WEW1-1000 WEW1-1600
WEW1-1600 WEW1-2000
WEW1-2000 WEW1-3200
WEW1-3200 WEW1-4000
WEW1-4000 WEW1-6300
WEW1-6300 DC6-125
DC6-125 AX-400-1250
AX-400-1250 AXAL-400-1250A
AXAL-400-1250A AL-400-1250
AL-400-1250 DC3-160
DC3-160 AXS-400-1250A
AXS-400-1250A SHT-125-160
SHT-125-160 UVT-125-160A
UVT-125-160A 400-3P/4P terminal cover
400-3P/4P terminal cover 1250-3Pmccb accessories busbar
1250-3Pmccb accessories busbar 250-3P terminal conver
250-3P terminal conver WLM6-TCV-160A-3P
WLM6-TCV-160A-3P WLM6-MIP-250A
WLM6-MIP-250A WLM6-125A-3300 3P/4P
WLM6-125A-3300 3P/4P WLM6-160A-3300 3P/4P
WLM6-160A-3300 3P/4P WLM6-250A-3300 3P/4P
WLM6-250A-3300 3P/4P WLM6-400A-3300 3P/4P
WLM6-400A-3300 3P/4P WLM6-630A-3300 3P/4P
WLM6-630A-3300 3P/4P WLM6-800A-3300 3P/4P
WLM6-800A-3300 3P/4P WLM6-1250A-3300 3P/4P
WLM6-1250A-3300 3P/4P WLM6-1600A-3300 3P/4P
WLM6-1600A-3300 3P/4P WLM6-2000A 3P/4P
WLM6-2000A 3P/4P WLM6RT-125A
WLM6RT-125A WLM6RT-160A
WLM6RT-160A WLM6RT-250A
WLM6RT-250A WLM6RT-400A
WLM6RT-400A WLM6RT-630A
WLM6RT-630A WLM6RT-800A
WLM6RT-800A WLM6RT-1250A
WLM6RT-1250A WLM6E-160A-3300 3P
WLM6E-160A-3300 3P WLM6E-250A-3300
WLM6E-250A-3300 WLM6E-400A-3300 3P/4P
WLM6E-400A-3300 3P/4P WLM6E-630A-3300
WLM6E-630A-3300 WLM6E-800A-3300 3P/4P
WLM6E-800A-3300 3P/4P WLM6E-1250A-3300
WLM6E-1250A-3300 WLM6E-1600-3300 3P/4P
WLM6E-1600-3300 3P/4P WLM6E-2000A-3300 3P/4P
WLM6E-2000A-3300 3P/4P WLM6EY-250-3300 3P/4P
WLM6EY-250-3300 3P/4P WLM6EY-400 3P/4P
WLM6EY-400 3P/4P WLM6EY-630 3P/4P
WLM6EY-630 3P/4P WLM6EY-800A 3P/4P
WLM6EY-800A 3P/4P WLM6EY-1250A 3P/4P
WLM6EY-1250A 3P/4P WLM6ELY-160A
WLM6ELY-160A WLM6ELY-250A
WLM6ELY-250A WLM6ELY-400A
WLM6ELY-400A WLM6ELY-800A
WLM6ELY-800A WLM6ELY-1250A
WLM6ELY-1250A WLM6LY-125A
WLM6LY-125A WLM6L-160A
WLM6L-160A WLM6LY-250A
WLM6LY-250A WLM6LY-400A
WLM6LY-400A WLM6LY-800A
WLM6LY-800A WLM6LY-630A
WLM6LY-630A WLM6LY-1250A
WLM6LY-1250A JCB3-63DC
JCB3-63DC JCB1-125DC
JCB1-125DC P-250A-3P-A
P-250A-3P-A WLM7DC-250A-2300 2P/3P
WLM7DC-250A-2300 2P/3P WLM7DC-315A-3300 2P/3P
WLM7DC-315A-3300 2P/3P WLM7DC-400A-2300 2P/3P
WLM7DC-400A-2300 2P/3P WLM7DC-630A-3300 3P
WLM7DC-630A-3300 3P WLM7DC-800A-2300 2P/3P
WLM7DC-800A-2300 2P/3P WLM7DC-400A 2300
WLM7DC-400A 2300 WLM7DC-630A-2300 2P
WLM7DC-630A-2300 2P WLM7HU-250-3300 3P
WLM7HU-250-3300 3P WLM7HU-315-3300 3P
WLM7HU-315-3300 3P WLM7HU-400-3300 3P
WLM7HU-400-3300 3P WLM7HU-630-3300 3P
WLM7HU-630-3300 3P WLM7HU-800-3300 3P
WLM7HU-800-3300 3P PV-1500V/250A
PV-1500V/250A WEW3-1600
WEW3-1600 WEW3-2500
WEW3-2500 WEW3-4000
WEW3-4000 WEW3-7500
WEW3-7500